JACKSONVILLE, FL—As treatment options for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) multiply, physicians face an increasing array of sequencing options but have little guidance from clinical trials of the most effective order given each patient’s specific disease characteristics, health status and preferences.
Researchers at the Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, FL, and colleagues sought to bring greater clarity to the choice and timing of therapies by conducting a retrospective, observational study of 3,431 patients diagnosed with CLL between Jan. 1, 2018, and January 1, 2023, using records sourced from the ConcertAI dataset of more than 6 million deidentified patients. The results of the study were presented at the 65th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting on Dec. 11.1
The team followed patients who received at least one line of therapy after diagnosis, until the first of the end of the health record or death. They grouped patients in four categories based on their treatment: chemotherapy, anti-CD20-based therapy, Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor-based therapy or venetoclax-based therapy.
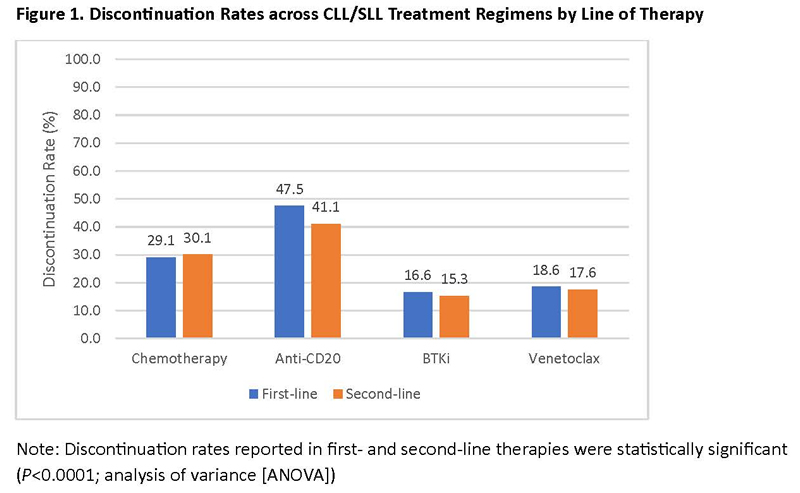
Chanan-Khan AA, Challagulla S, Kaushiva A, Miller V, Wang Y, Smith H, Yang K. Impact of Real-World Treatment Sequencing Patterns on Time to Next Treatment among Patinets with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in the United States. Abstract 5143. ASH 2023. Dec. 11, 2023.
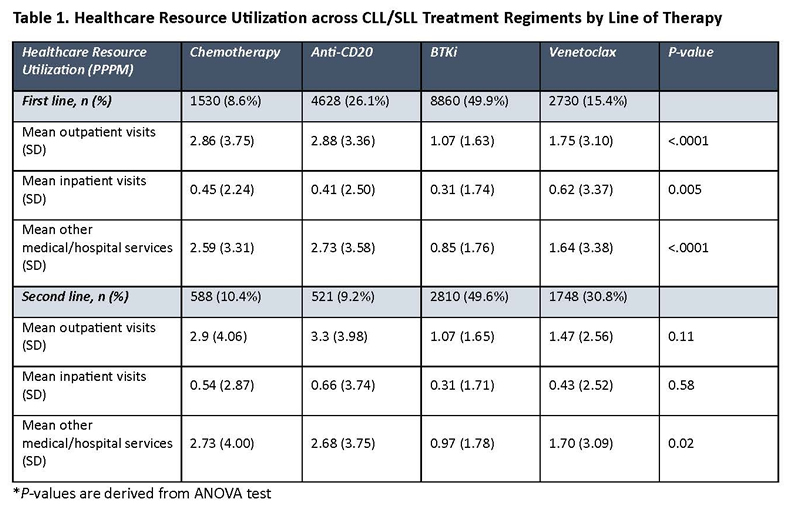
Chanan-Khan AA, Challagulla S, Kaushiva A, Miller V, Wang Y, Smith H, Yang K. Impact of Real-World Treatment Sequencing Patterns on Time to Next Treatment among Patinets with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in the United States. Abstract 5143. ASH 2023. Dec. 11, 2023.
The researchers noted a significant variation in average age between the groups, with those receiving anti-CD20-based therapy having a median age of 71 years, while those who received venetoclax-based therapy were somewhat younger than the overall population at 67 years. The overall study population was predominantly male (63.8%) and treated in community settings (76.4%).
BTK inhibitors (ibrutinib, acalabrutinib or zanubrutinib) were the most common choice in the first-line at 60.1%, followed by venetoclax (16%) and anti-CD20 therapies (15.4%). Zanubrutinib, which just gained approval in January 2023 and so was not commercially available during the study, was selected in 2.6% of cases that started with BTK inhibitors.
Thirty-five percent of patients proceeded to a second line, and BTK inhibitors continued to be the leading choice at 35.7%, with anti-CD20 therapies used for 29.6% of patients and venetoclax for 25.8%.
The most common sequence between the first and second line was from one BTK inhibitor to another (23.5%). Switching from venetoclax to anti-CD20 occurred in 13.2% of cases and from BTK inhibitors to an anti-CD20 in 9.7%. Between the second and third line, the most common progression was from anti-CD20 to venetoclax (24.6%). Switching from anti-CD20 therapy to a BTK inhibitor occurred in 13.3%, and about an equal number moved from one BTK inhibitor to another in 12.6% of patients.
Between the third and fourth lines, the most common patterns were a shift from venetoclax to anti-CD20 therapy, which occurred in 21.3% of cases or from an anti-CD20 back to venetoclax, which happened in 20.6% of patients. Just over 11% of patients switched between BTK inhibitors at this point.
Notably, BTK inhibitors provided the longest median time to next treatment in the first line at 53.9 months, nearly seven times longer than seen in patients treated first with venetoclax (7.7 months). In the second line, patients who received BTK inhibitors had not reached a median time to next treatment, while in those who received venetoclax it was 10.4 months and for anti-CD20 only 1.5 months.
“As the most commonly used regimen, BTKi therapy was shown to have significantly improved time to next treatment compared with other treatment regimens in first and second lines of therapies,” the researchers concluded. “Future studies with extended follow-up are needed to allow for assessment of newer treatments and enable evaluation of long-term clinical outcomes.”
1Chanan-Khan AA, Challagulla S, Kaushiva A, Miller V, Wang Y, Smith H, Yang K. Impact of Real-World Treatment Sequencing Patterns on Time to Next Treatment among Patinets with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in the United States. Abstract 5143. ASH 2023. Dec. 11, 2023.

